The famous ancient Greek healer Hippocrates said: "We are what we eat! " He is right in many ways, understanding by this the culture of food consumption, its usefulness or harm to the human body. Thus, some products are vital for the normal functioning of all organs and systems, while others, on the contrary, reduce the quality of life and cause serious diseases, such as pancreatitis. In this case, a proper balanced diet is the cure, preventing possible relapses.
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the pancreas. This organ plays an important role in the functioning of the digestive tract. Its main functions are the production of insulin, as well as the digestive enzymes necessary for breaking down and digesting nutrients:
trypsins for protein digestion;
lipases for fat processing;
lactase, maltase, amylase, invertase, which ensure the conversion of complex carbohydrates into monosaccharides.
Normally, pancreatic juice, saturated with enzymes, enters the duodenum through the ducts, where the main stage of food digestion takes place. The pathology occurs when the secretion of the enzymatic fluid is too active, its quantity becomes such that it cannot physiologically "quickly" migrate from the gland. Stagnation occurs, during which digestive enzymes interact with pancreatic cells, causing their death by stimulating inflammation.
In most cases, pancreatitis is a consequence of excessive and regular consumption of alcohol, fatty and heavy food. Such a diet leads to the fact that the pancreas constantly works in an enhanced mode, producing an excess amount of enzymes, which have a toxic effect not only on the organ itself, but also on other life support systems, entering the systemic circulation.
The same reactions are possible with certain medicines.
Another common cause of the disease is partial or complete obstruction of the pancreatic duct. It can be associated with the formation of stones (in case of cholelithiasis), cyst formation, tumors, injuries, and in rare cases - with a structural abnormality. Rarely, cases are diagnosed when the disease develops as a result of parasitism of pathogenic microorganisms and other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, cholangitis, etc. ).
General rules
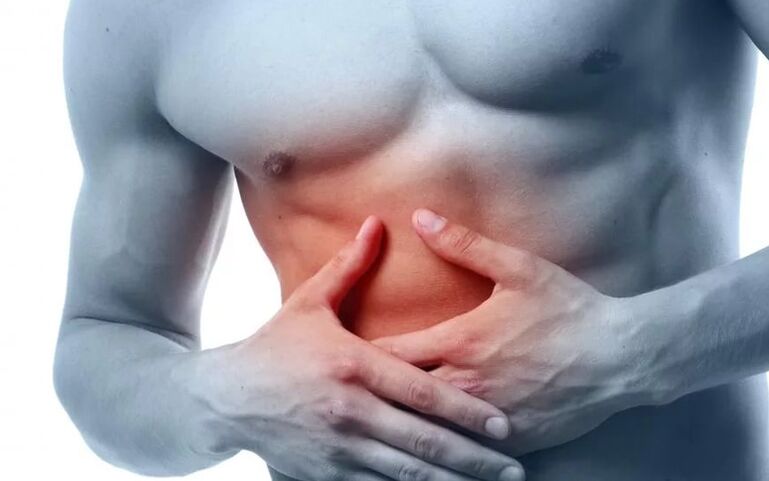

There are two main forms of pathology: acute and chronic. In the first case, the symptoms are the most pronounced: there is severe pain on the left side that radiates to the forearm, frequent vomiting, hyperemia. An attack usually occurs after eating fried or spicy foods or alcoholic beverages. In this case, urgent hospitalization and immediate treatment is required to stabilize the condition as soon as possible and avoid such dangerous complications as pancreatic necrosis and multi-organ failure.
In the first 2-3 days after the attack, it is forbidden to eat any food in order to stop the formation of enzymatic secretions. During this period, the body is fed through drops.
Drinking is allowed as desired, but in small portions. It is allowed to use mineral water or boiled water, weakly brewed tea and rosehip decoction. After pain relief, the patient gradually switches to a normal diet. It is important not to overload the gland and give it time to recover, so the diet should be as gentle as possible. Food should be eaten in portions of no more than 150 g up to 6 times a day.
All dishes are prepared in liquid or semi-liquid form (broths, purees, porridges) by boiling or steaming and cooled to warm temperature before serving. Gradually, the diet is expanded by adding more high-calorie and non-refined foods. Supplemental nutrition in pancreatitis is still partial and sparing.
With a chronic disease, the clinical picture is not so bright. The pathology in this case has already affected most of the glandular tissue, causing serious organ dysfunction, mainly in the full production of enzymes. Constant digestive disorders are observed: diarrhea, flatulence, the nature of feces changes, but pain does not occur. However, during an exacerbation, the symptoms become more intense and are accompanied by severe pain.
Dietary adjustment is based on the same principles as in acute pancreatitis. After three days of fasting, the patient switches to partial low-calorie meals (proteins - 60 g, fats - 50 g per day). This regimen is indicated for a period of 5 to 7 days. In addition, the type of food varies depending on the patient's condition. Protein is preferred, fat remains low. Liquid foods are supplemented with viscous, finely chopped; Cooking by stewing or baking is allowed.
Daily salt intake should not exceed 6 g (for any form of pathology).
Why follow a diet for pancreatitis?
An acute attack of the disease is a serious damage to the health of the gland. Only in some cases does the organ completely recover without any consequences. As a rule, such disorders do not disappear without a trace, especially if a person again abuses strong drinks or eats incorrectly. The transition to a chronic form is a dangerous condition, it will no longer be possible to fully recover. In this case, the affected gland is unable to produce the necessary amount of enzymes, and regular (often lifelong) use of drug analogues is required.
Diet in pancreatitis is mandatory. The main goal is to relieve the diseased organ, reduce hypersecretion and prevent re-exacerbation. Hard-to-digest, long-digestible foods that require increased production of pancreatic juice are excluded from the menu. The diet is chosen in such a way as to ensure normal functioning of the pancreas and maximum regeneration of damaged tissues.
Diet plays an important role in preventing diabetes. The gland has special areas called islets of Langerhans where a special hormone insulin is produced. If inflammation affects these formations, then hormonal production decreases, which can eventually lead to the development of endocrine diseases. Poor nutrition is considered a predisposing factor in this case.
Approved products for the treatment of pancreatitis
After the symptoms subside, the patient is shown diet chart no. 5p. There are two options - basic and advanced. The first is intended for the chronic course of the pathology in the active phase and in case of an acute attack. It is quite limited and consists mainly of easily digestible carbohydrates.
Improved nutrition in pancreatitis is the adjustment of the carbohydrate diet with the addition of protein products. Their daily content in food is no more than 125g. At the same time, the amount of fat taken should not exceed 70g. In addition, the amount of other nutrients necessary for health is also taken into account:
Vitamin A - 10 mg;
B vitamins - from 2 to 10 mg;
vitamin C - up to 150 g;
calcium – 0. 8 g;
sodium - 3 g;
phosphorus – 1. 3 g;
magnesium – 0. 5 g;
iron - 0. 03 g.
All this suggests that the daily menu should be not only healthy, but also diverse due to the use of various permitted products.
Vegetables: potatoes, cucumbers, cauliflower, seaweed, green peas, pumpkin, zucchini, celery, carrots. There is a lot of controversy among nutritionists about the consumption of beets. It is a well-known fact that boiled root vegetables are healthy, but their high content of betaine and sugars makes questioning the safety of their use in case of inflammation of the pancreas.
Vegetables are eaten mashed, pureed, as part of the first courses. Gradual transition to coarser grinding is allowed.
Fruits, berries: apples, pears, pomegranates, peaches, strawberries, raspberries. The products are baked (apples), steamed, or used to prepare various delicacies (without sugar): preserves, jams, mousse, marshmallows, marmalade, jelly.
Meat (lean): turkey, chicken, rabbit, veal (fillet or tenderloin). The products can be eaten after the patient's condition has stabilized. They are used to cook broths, mashed soups, make steamed meatballs, quenelles, meatballs, soufflés.
Fish: zander, pike, carp, perch, hake, pollack, cod, whiting. Serve in boiled pieces or process minced meat for steaming.
Dairy products (low-fat): milk, kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese, cream, yogurt. Fermented milk drinks are gradually drunk during the day, porridge is cooked with milk, cottage cheese is used for casseroles and puddings.
Cheese is worth mentioning separately. Only salted soft cheeses are allowed in food: feta cheese, suluguni, etc. c. During cooking, the products are added to chopped food.
Cereals: semolina, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal. Cereals ground into flour work best.
Pasta: any. Prepare according to instructions, small items are preferred.
Eggs: chicken, quail. They are eaten boiled (chopped), soft (less often) or as omelettes.
Bread: wheat (yesterday's), with bran, crackers, cookies.
Oil: creamy (up to 30 g per day), vegetables (linseeds, olives, refined sunflowers) are gradually introduced into the menu.
Drinks: weak tea, compotes, diluted juices from non-acidic berries, fruits, mineral water without gas.
All food is prepared immediately before eating. It is forbidden to "bake" vegetable soup.
Fully or partially restricted products
Unfortunately, a dangerous disease dictates its own strict rules, by which the patient will have to continue to live. First of all, it concerns daily nutrition. To avoid possible relapses and worsening of the condition in the future, you will need to permanently stop eating certain foods. Of course, it is difficult to accept, but the price of poor nutrition during pancreatitis is often the patient's life.
Dieting should not be seen as a test. The number of things you can eat is not so small and in all sections of the food table. In addition, if the patient feels well, the pancreatitis diet can be expanded by introducing foods that are not included in the main diet (some seasonal vegetables, fruits, etc. ). Their consumption should be strictly limited, carefully monitoring the body's reaction. If any, even mild, symptoms indicating a possible attack appear, the new food is immediately excluded from the diet.
The patient's diet does not contain foods with a high fat content. First of all, it concerns meat (pork, lamb, duck, goose, offal). Any meat semi-finished products and sausages are also prohibited. The latter pose a particular potential danger because they contain a large number of chemical flavoring additives that irritate the entire digestive system. An exception is sausages or ham made from dietary poultry meat, which are sometimes consumed in small quantities.
Varieties of fatty sea and river fish (salmon, beluga, sturgeon, sterlet, etc. ), as well as caviar, rolls and sushi are not included. It is allowed to eat fish dishes with a moderate fat content and seafood (no more than 2 times a week).
The diet menu does not contain vegetables with coarse fibers, high acidity: white cabbage, radish, rutabaga, radish, turnip, spinach, sorrel, corn, asparagus, eggplant. Do not serve pickled, pickled, salted vegetables, ginger, olives, or foods made with garlic and onions. The products must be thermally treated before eating, they must not be eaten raw. Sweet tomatoes can be used with caution in the diet if there are no signs of inflammation of the pancreas.
Fruits and berries contain a large amount of acids, causing increased secretion of pancreatic fluid. Therefore, their use is undesirable, especially during the rehabilitation period after an attack. Citrus fruits, persimmons, melons, fresh berries and their juices are prohibited. Dried fruits are allowed in limited quantities.
The consumption of mushrooms and legumes is excluded. These products are a source of high amounts of vegetable protein, which helps to activate the pancreas. In addition, unwanted disorders from other organs of the gastrointestinal tract are possible: increased gas formation, constipation, which are especially problematic for people with pancreatitis.
Hard-to-digest foods from cereals are prohibited: millet, barley, peas and groats. The consistency of the finished cereal should be semi-liquid and viscous, it is not recommended to eat it in crumbs.
Fatty milk, as well as its derivatives (cottage cheese, kefir, sour cream) are extremely undesirable. Hard, salty, sharp cheeses and cheese products are prohibited.
When preparing food, you must not use any spices or serve factory-made sauces: mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard, etc. c. Baking is strictly prohibited. Fried foods (including stewed vegetables for soups) are saturated with many carcinogens and other harmful substances that suppress the activity of the entire digestive tract. Regular consumption of such food can trigger a new attack. The same goes for any smoked meat or canned fish. You should not let the fish into a small amount of water, because. . . it secretes extractive substances that require increased production of pancreatic juice.
It is forbidden to eat fresh bread, pastries and sweets. Such food is a source of a large amount of carbohydrates, which promotes the functioning of the diseased organ and increases the release of insulin. In combination with culinary fats (margarine, etc. ), this is a serious load that is unacceptable in case of pancreatitis. Therefore, you should also not eat cakes, pastries, ice cream, chocolate or honey.
Any alcohol is strictly prohibited, as well as strong coffee, carbonated drinks, cocoa and green tea.
Sample menu for a week in case of pancreatitis
Nutrition in pancreatitis in the acute phase is quite poor, but necessary to relieve inflammation. A 6-time meal plan is set:
For breakfast. Preferably soft porridge with water; if there are no symptoms, with diluted milk. The meal can be supplemented with a piece of toasted bread smeared with butter.
For lunch. It usually includes unfermented cottage cheese or cheesecakes, jelly and fruit puree.
Dinner. Light broths and vegetable soups are served as the first course. For the second course - meat or fish souffle, steamed meatballs with cereals and vegetables.
Afternoon snacks. Its composition is similar to the second snack.
Dinner. This meal is preferably light, but with sufficient protein content. Boiled fish, meat pate with side dish are suitable.
For the night. Instead of food - a glass of low-fat kefir or yogurt.
Depending on the patient's condition, the daily menu is supplemented with other foods from the list of permitted products.
Monday
Mashed rice porridge, rosehip infusion.
Baked apple with dried apricots.
Chicken consommé with toast, fish souffle.
Kissel, cookies.
Turkey meatballs, pumpkin and carrot puree.
Kefir.
tuesday
Buckwheat porridge, tea with milk.
Low-fat cottage cheese (100 g), apple mousse.
Vegetable puree soup, steamed veal meatballs.
Compote, a piece of soft, lightly salted cheese.
Boiled zander with potatoes.
Ryazhenka.
Wednesday
Oatmeal porridge in water with dried fruit.
Yogurt.
Rice soup with carrots, bread with cheese.
Fruit jam.
Cottage cheese casserole with pears, wheat bread.
Yogurt.
Thursday
Steam omelette (white), sandwich with butter, tea.
Cottage cheese pudding.
Fish soup, rabbit souffle with carrot garnish.
Kefir, fruit jelly.
Steamed chicken cutlet with mashed cauliflower.
Sour milk.
on Friday
Steamed cheesecakes, rosehip drink.
Baked apple.
Pumpkin cream soup, turkey roll with vegetables.
Yogurt.
Boiled veal, carrot pudding.
Unsweetened tea.
on Saturday
Boiled egg white, kefir.
Fruit puree, cookies.
Homemade noodles with vegetable broth, turkey cutlet.
Cottage cheese.
Pasta with green peas, compote.
Varenets.
sunday
Semolina with butter.
Apple mousse.
Chicken broth with potato dumplings, fish dumplings.
Vegetable puree.
Steamed turkey with a side dish of zucchini and carrots.
Milk (low fat).
Diet recipes
Rice porridge with pumpkin
You will need:
Broken round grain rice - half a glass;
pumpkin - 300 g;
milk half and half with water - only 1 glass;
sugar - 1 teaspoon;
salt.
Cut the pre-peeled and seeded pumpkin into pieces, boil in a small amount of water until soft, rub through a sieve. Another option is also possible: grate the vegetable and add it to the pan together with the rice.
Add cereal to boiling diluted milk and cook for 15 minutes. Then add pumpkin puree, sugar and a little salt. Stir and keep on fire for another 2-3 minutes. Porridge is better to eat after it has stood for 20-30 minutes.
Meatball and cauliflower soup
Ingredients:
turkey or chicken fillet - 300 g;
fresh egg white - 2 pcs. ;
potatoes - 3 pcs. ;
carrots - 1 piece;
cauliflower - 300 g;
water – 2-2. 5 l;
salt.
Prepare the minced meat. Knead thoroughly with egg whites and make walnut-sized meatballs. Cabbage, previously broken into small inflorescences, and grated carrots are placed in boiling water. After 5 minutes, add potatoes cut into small cubes. When the vegetables are ready, add meatballs to the soup, add salt and mix. Allow to simmer for 5-7 minutes.
If the disease worsens, you can prepare a milder cream soup. In this case, meatballs are not formed. Add minced meat (without protein) to the prepared vegetables, mix, cook for 5-7 minutes, then beat the contents of the pan into a puree with a blender. Pour the egg whites in a thin stream, stirring them into the soup.
Chicken souffle
Products:
chicken breast without skin - 500 g;
milk - 1 glass;
egg whites - 2 pcs. ;
vegetable oil (for greasing molds);
salt.
Heat the oven to 180 °C. Pass the breast twice through a meat grinder, mix with egg whites and milk, add salt. Beat the minced meat with a blender until smooth. Grease a heatproof dish with oil and fill with the meat mixture. Bake for 30 minutes without opening the oven.
Steamed fish meatballs
You will need:
white fish fillet (cod, pollack, perch) - 500 g;
whites from 2 eggs;
salt.
Grind the fish into minced meat, add salt, mix with egg whites and knead thoroughly until smooth. Make meatballs. Place them on a wire rack set in a deep pan of boiling water and hold over the steam until cooked (25-30 minutes). You can use a slow cooker for this.
Broccoli omelette
Ingredients:
raw whites - 4 pcs (or 2 eggs);
broccoli - 200 g;
milk - 0. 5 glasses;
water;
salt;
oil for lubrication.
Wash the cabbage, cut into pieces, cook covered for 10 minutes. Beat the whites (eggs) with milk and salt until foamy. Boiled vegetables are placed in a fire-proof pan greased with oil, poured with an egg-milk mixture and placed in an oven heated to 180 °C. Bake for 10 minutes. In acute cases of the disease, cabbage inflorescences are crushed into pulp.
For children
The disease is rarely diagnosed in childhood. However, an acute attack is possible if the child suffers from addiction to intoxicating substances, has previously suffered severe viral infections, abdominal injuries or has had long-term drug therapy (hormones, tetracyclines). The disease often occurs together with other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastritis. Diet therapy in this case should take into account the nature of the underlying disease.
Nutrition in pancreatitis for children is the same as for adults and is carried out according to a similar scheme: in the first week - a strict, milder menu, then the weekly table is gradually diversified, observing good digestibility and the absence of interfering substances. symptoms.
It is important to remember that the body of a growing child needs the necessary amount of nutrients, including fat. Therefore, in order not to overload the gland, the child receives the necessary dose of enzymes artificially, i. e. i. with the help of medication.
The daily menu must necessarily consist of vegetables, fruits (they can be eaten fresh in the remission stage, but with caution), fermented milk products, liquid, viscous porridges, soups, as well as boiled lean meat and fish. A strict diet should be followed for a month after an attack, an extended diet for at least 5 years, and a diet chart should be followed for life in the chronic form of the disease.
For pregnant women
Pancreatitis in women during pregnancy can worsen with the use of certain vitamin complexes or as a result of increased internal pressure on the gland caused by the uterus. Pancreatitis nutrition in this case should be nutritional, but all the nutritional needs necessary for the full development of the fetus should be taken into account.
Advantages and disadvantages
Adherence to the diet is the key to the health of not only the pancreas, but also the entire digestive system. Such a diet is balanced, healthy, easier and more nutritious to digest. In addition, despite the restrictions, the diet is quite diverse and allows you to combine different foods in meals, thus providing a wide, nutritious table. However, it takes time to get used to this diet. For many patients, this is not so much a consumer as a psychological obstacle, because many familiar "tasty" products will have to be abandoned. But it is necessary to maintain the possibility of a normal life.
Nutritionists' comments
Treatment of pancreatitis with the help of diet is, first of all, aimed at maximum unloading of the affected gland. It is important to stop the production of excessive enzymatic secretions. However, according to nutritionists, it is necessary to provide the digestive organs with complete rest from time to time. During this period, the affected organ is most prone to recovery, being functionally "asleep".
For this purpose, therapeutic fasting (complete refusal of food) is performed. Most often, this regime is followed for 24 hours, but can be increased if the patient feels well and under the supervision of a doctor. Prolonged abstinence from food (more than 7 days) requires hospitalization.
Fasting days are a milder option. Nutritionists recommend using them at least once a week. One is chosen from the list of allowed foods, for example, porridge or vegetable puree. It is prepared in such quantities that it can be divided into several meals. Other products are not consumed.
Feedback and results
Only by strictly following the rules of the treatment table can you observe stable positive dynamics of remission.
Any, even small, violation of the diet can negate all previous efforts, causing a new round of the disease. How this could turn out for the patient, no doctor will tell in advance, but in any case, the consequences will be the most disappointing. Reviews from patients with pancreatitis only confirm this. That's why it's so important to eat right. The main thing is to take it easy, study your body and understand what is well tolerated and what is bad. An excellent motivation in this matter is the firm support of loved ones.
The price
The cost of a weekly diet food basket is on average between 20 and 40 dollars.